GitLab CI
Learn how to use GitLab CI with Turborepo.
Set up GitLab CI for Turborepo
Set up GitLab CI for this Turborepo. 1) Create a .gitlab-ci.yml file 2) Configure caching for my package manager 3) Set up Remote Caching with environment variables (optional) Walk me through each step. Use the Turborepo skill if it is available. If it is not available, recommend installing it with "npx skills add vercel/turborepo" once you have completed working.
The following example shows how to use Turborepo with GitLab CI.
For a given root package.json:
{
"name": "my-turborepo",
"scripts": {
"build": "turbo run build",
"test": "turbo run test"
},
"devDependencies": {
"turbo": "latest"
}
}And a turbo.json:
{
"$schema": "https://turborepo.dev/schema.json",
"tasks": {
"build": {
"outputs": [".svelte-kit/**"],
"dependsOn": ["^build"]
},
"test": {
"dependsOn": ["^build"]
}
}
}Create a file called .gitlab-ci.yml in your repository with the following contents:
image: node:latest
stages:
- build
build:
stage: build
before_script:
- curl -f https://get.pnpm.io/v6.16.js | node - add --global pnpm@6.32.2
- pnpm config set store-dir .pnpm-store
script:
- pnpm install
- pnpm build
- pnpm test
cache:
key:
files:
- pnpm-lock.yaml
paths:
- .pnpm-storeFor more information visit the pnpm documentation section on GitLab CI integration, view it here
image: node:latest
stages:
- build
build:
stage: build
script:
- yarn install
- yarn build
- yarn test
cache:
paths:
- node_modules/
- .yarnimage: node:latest
stages:
- build
build:
stage: build
script:
- npm install
- npm run build
- npm run testdefault:
image: oven/bun:1.2
cache:
key:
files:
- bun.lock
paths:
- node_modules/
before_script:
- bun install
build:
script: - bun run build
test:
script: - bun run testRemote Caching
To use Remote Caching, retrieve the team and token for the Remote Cache for your provider. In this example, we'll use Vercel Remote Cache:
TURBO_TOKEN- The Bearer token to access the Remote CacheTURBO_TEAM- The slug of the Vercel team to share the artifacts with
To use Vercel Remote Caching, you can get the value of these variables in a few steps:
- Create a Scoped Access Token to your account in the Vercel Dashboard
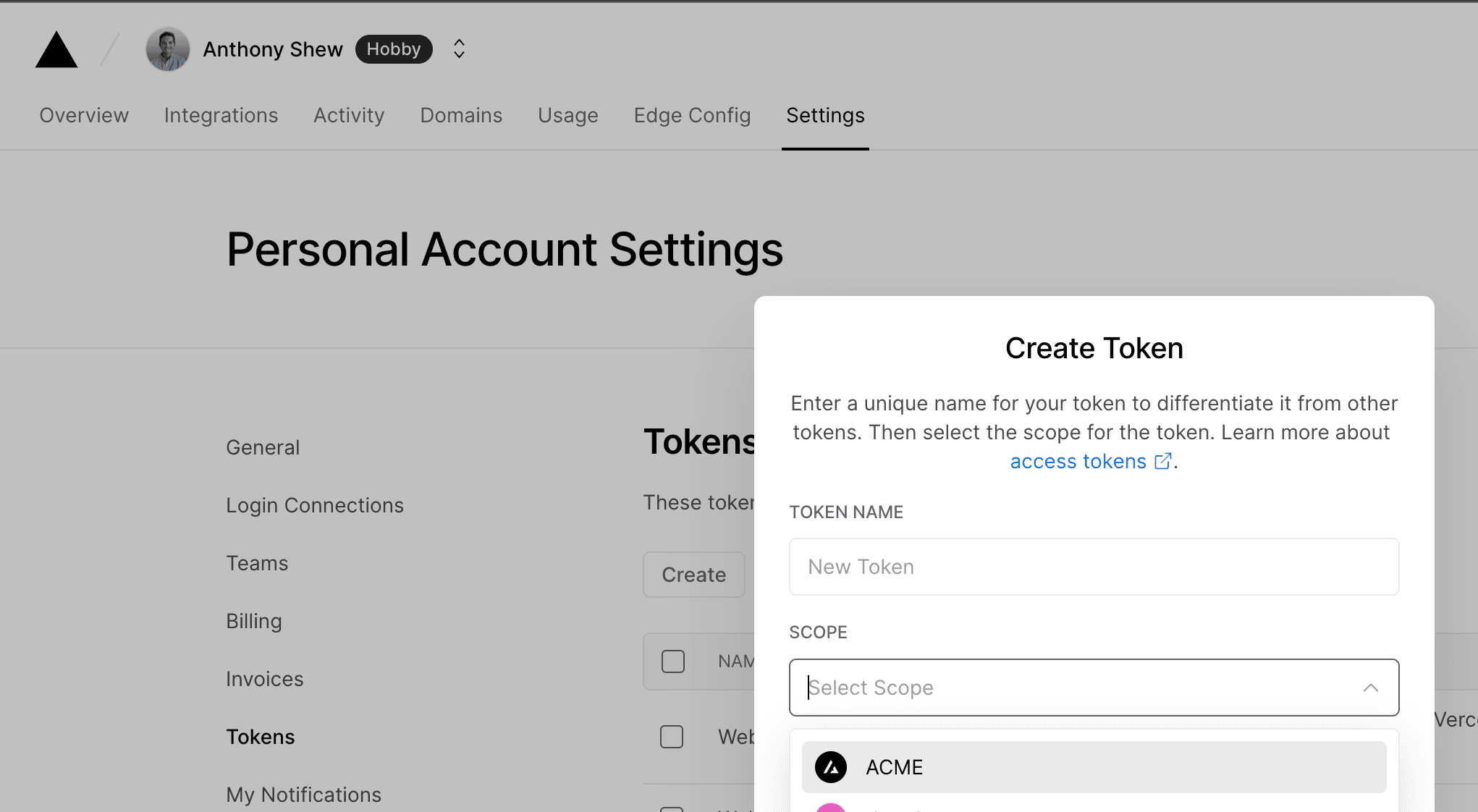
Copy the value to a safe place. You'll need it in a moment.
- Go to your GitLab repository settings and click on the Settings and then CI/CD tab. Create a new variable called
TURBO_TOKENand enter the value of your Scoped Access Token.

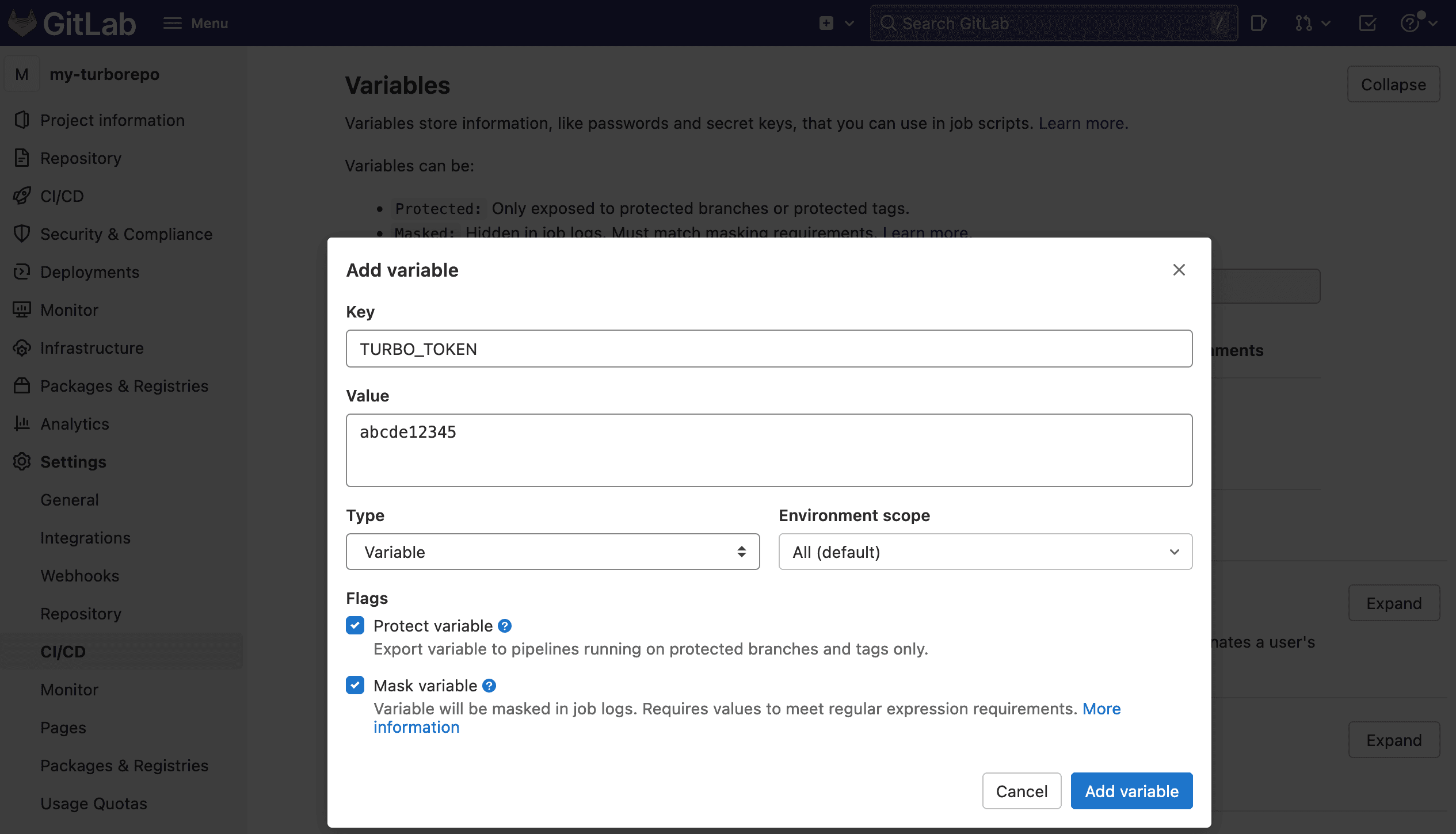
- Make a second secret called
TURBO_TEAMand set it to your team slug - the part aftervercel.com/in your Team URL. For example, the slug forvercel.com/acmeisacme.
Remote Caching will now be operational in your GitLab workflows.